The History of Electric Motors
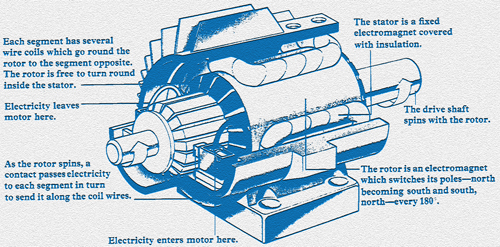
In the 1830’s, Michael Faraday made a discovery that has made work easier for all of us. While experimenting with magnets he found that moving a wire through a magnetic field would produce an electric current. This experiment is important because it led to the discovery of the operating principles of electric motors and generators.
A motor is a rotating machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. A generator, on the other hand, is a rotating machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Electric motors play a very important part in furnishing power for all types of domestic and industrial applications. Their versatility, dependability, and economy of operation cannot be equaled by any other form of motive power.
These motors, the machine they drive, and motor controller are interrelated. They need to be considered a package when choosing a specific device for a particular application.
In general, five basic factors influence the selection of a controller:
- Electric Service-Establish whether the service is dc or ac. If ac, determine the number of phases and the frequency-in addition to the voltage.
- Motor-The motor should be matched to the electrical service. The motor should be correctly sized for the machine load (horsepower rating). Other considerations include the motor speed and torque. To select the proper protection for the motor, it’s full load current rating, service factor, and time rating must be known.
- Operating Characteristics of the Controller-The fundamental job of a motor controller is to start and stop the motor. It should also protect the motor, machine, and operator. The controller might also be called upon to provide other functions, which could include varying the motor speed, current and torque; reversing, jogging or inching.
- Environment-Controller enclosures serve to provide protection for the operating personnel by preventing accidental contact with live parts. In certain applications the controller itself must be protected from weather, dirt or dust, oil or other contaminants.
- National codes and Standards-Motor and motor control equipment are designed to meet the provisions of the National Electrical Code (NEC);
Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA)
National Electric Manufacturers Association (NEMA)
Underwriters Laboratories (UL)
Each of which provide safety and practical information in the application of electric motors and controls.
There are new governmental standards on efficiency of electric motors (IEE-84I ).
Contact Priest Electric For All Your Electric Motor Needs – Servicing Boise, Nampa, Caldwell, All of Idaho, Nevada, and Oregon

Leave A Comment